Frequently Asked Questions
What is the SCO?
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a permanent intergovernmental international organisation.
The main goals of the SCO are strengthening mutual confidence and good-neighbourly relations among the member countries; promoting effective cooperation in politics, trade and economy, science and technology, culture as well as education, energy, transportation, tourism, environmental protection and other fields; making joint efforts to maintain and ensure peace, security and stability in the region, moving towards the establishment of a new, democratic, just and rational political and economic international order.
Proceeding from the Spirit of Shanghai the SCO pursues its internal policy based on the principles of mutual trust, mutual benefit, equal rights, consultations, respect for the diversity of cultures and aspiration towards common development, its external policy is conducted in accordance with the principles of non-alignment, non-targeting anyone and openness.
History of the SCO
About creation of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) was proclaimed on June 15, 2001 in Shanghai (China) by the Republic of Kazakhstan, the People's Republic of China, the Kyrgyz Republic, the Russian Federation, the Republic of Tajikistan and the Republic of Uzbekistan.
Prior to that, all of the above countries, except for Uzbekistan, were members of the Shanghai Five, a political association based on the Agreement on Confidence-Building in the Military Field in the Border Area (Shanghai, 1996) and the Agreement on the Mutual Reduction of Armed Forces in the Border Area (Moscow, 1997). These two documents laid down a mechanism of mutual trust in the military sphere in the border area and contributed to the establishment of true partnerships. Following the accession of Uzbekistan to the organisation in 2001, the Shanghai Five was renamed the SCO.
Initially, the SCO focused on mutual intraregional efforts to curb terrorism, separatism and extremism in Central Asia. The Charter of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation was signed at the St.Petersburg Summit of the Heads of State of the SCO in June 2002 and entered into force on 19 September 2003. It is a fundamental constituent document stipulating the objectives and principles of the Organisation, its structure and its primary areas of activities. In addition, the SCO plans to combat international drug trafficking as a source of financing global terrorism were announced in 2006; in 2008, the Organisation actively participated in normalising the situation in Afghanistan.
At the same time, the SCO took up a variety of economic activities. In September 2003, the heads of the SCO member states signed a 20-year Programme of Multilateral Trade and Economic Cooperation. As a long-term goal, the programme provides for the establishment of a free trade zone within the territory under the SCO member states; in the short run, it seeks to reinvigorate the process of creating favourable environment for trade and investment.
Which countries are members of the SCO?
Currently, six countries enjoy the status of the SCO full members: Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan; five countries - Afghanistan, India, Iran, Mongolia and Pakistan - have an observer status with the SCO, and three countries - Belarus, Turkey and Sri Lanka - have a dialogue partner status.
How many meetings of the SCO Heads of State Council have been held?
In all, 14 meetings of the Council of Heads of Member States of the SCO were held:
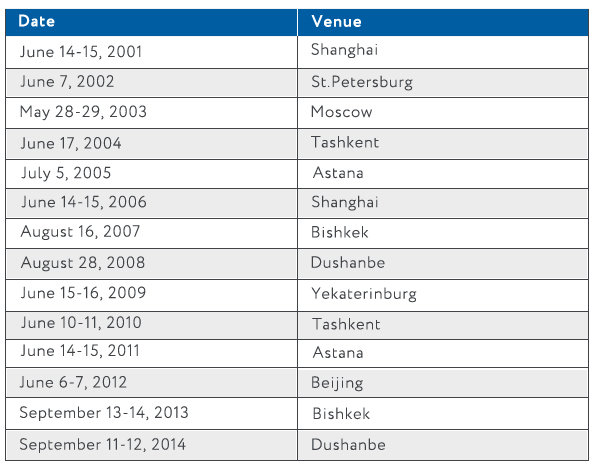
The 15th meeting of the Council of Heads of Member States of the SCO will take place in Ufa, Russia, in 2015.
How does the SCO work?
The Heads of State Council (HSC) is the highest decision-making body in the SCO. It meets once every year to take decisions and give instructions on all important issues regarding SCO activity.
The Heads of Government Council (HGC) meets once per year to discuss a strategy for multilateral cooperation and priority directions within the Organisation's framework, to solve important and pressing cooperation issues in economic and other areas, as well as to adopt the Organisation's annual budget.
In addition to sessions of the HSC and HGC, there are also mechanisms of meetings on the level of Speakers of Parliament, Secretaries of Security Councils, Foreign Ministers, Ministers of Defence, Emergency Relief, Economy, Transportation, Culture, Education, Healthcare, Heads of Law Enforcement Agencies, Supreme Courts and Courts of Arbitration, and Prosecutors General.
The Council of National Coordinators of SCO Member States (CNC) is in charge of coordinating interaction within the SCO framework.
The Organisation has two permanent bodies - the Secretariat in Beijing (China) and the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) in Tashkent.
The SCO Secretary-General and RATS Executive Committee Director are appointed by the HSC for a period of three years. Since 1 January 2013, these posts are held by Dmitry Mezentsev (Russia) and Zhang Xinfeng (China), respectively.
Russian and Chinese are the official working languages of the SCO.
What is the SCO RATS?
The Executive Committee of the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is the permanent body of the SCO RATS based in Tashkent, the capital of Uzbekistan.
The Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure operates in accordance with the SCO Charter, the Shanghai Convention on Combating Terrorism, Separatism and Extremism, the Agreement among the SCO member states on the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure, as well as documents and decisions adopted in the SCO framework.
What is the SCO Business Council?
The Business Council of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation was founded on June 14, 2006 in Shanghai. It is a nongovernment entity that unites the highly authoritative business community representatives of the SCO member states with an eye towards expanding economic cooperation, establishing direct relations and a dialogue between the business and financial communities, and facilitating the practical promotion of multilateral projects. In addition to energy, transport, telecommunications, lending and the banking sector, the council focuses on such priorities of interstate cooperation between the SCO countries as education, research and innovative technology, as well as healthcare and agriculture.
The SCO Business Council is an independent institution capable of taking advisory decisions and giving expert assessments regarding the involvement of members of the business communities of the SCO member states in trade, economic and investment interaction within the framework of the Organisation.
Annual Session is the highest body of the Business Council that sets priorities and formulates the primary targets for its activity and decides on important issues concerning links with business associations from other states.
The SCO Business Council's Permanent Secretariat is headquartered in Moscow.
What is the SCO Interbank Consortium?
The SCO Interbank Consortium (SCO IBC) was established by the Council of Heads of Government on 26 October 2005 to provide funding and bank services for investment projects sponsored by the governments of the SCO member states. The SCO IBC Council meets ad hoc upon the consensus of all of the parties at least once per year. The Presidency of the Council is carried out on a rotational basis.
The members of the SCO IBC are the Development Bank of Kazakhstan, the State Development Bank of China, the Settlement & Savings Company of the Kyrgyz Republic "RSK Bank", the Bank for Development and Foreign Economic Affairs of the Russian Federation "Vnesheconombank", the State Savings Bank of the Republic of Tajikistan "Amonatbonk", and the National Bank for Foreign Economic Activity of the Republic of Uzbekistan.
The priority areas of cooperation within the SCO IBC include: providing funding for projects that focus on the infrastructure, basic industries, high-tech industries, export-oriented sectors, and social projects; issuing and making loans based on the generally accepted international banking practices; organising pre-export financing to stimulate trade and economic cooperation between the SCO Member States, and other areas of common interest.
Host Photo Agency
The Host Photo Agency will provide high-quality photo images from all Presidency events which are open to the press. Photographs will be posted in the photo section of the official website of Russia's SCO Presidency immediately after the events.
Photos will be available for free download from the official website in high resolution. When publishing photos sourced from the official website a link to sco-russia2015.ru should be included.